
Protector of the security in the digital world
Knowledgebase
Contacts
- Lingkaran Sunway Velocity, Sunway Velocity, 55100 Kuala Lumpur, Wilayah Persekutuan Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
- +60163388502
- admin@abchost.cc
Hyper-V and Proxmox are type-1 (bare metal) hypervisors, which means they run directly on the host's hardware, using its resources to manage guest operating systems.
Note: Even though Hyper-V can be installed on bare metal, many of the advanced features are only available if the Hyper-V role is set up on top of Windows Server, whereas Proxmox doesn't require a base OS to unlock all of its tools.
Proxmox
Proxmox VE is an open-source enterprise-class server virtualization platform. It is based on Debian Linux and tightly integrates the KVM hypervisor and Linux Containers (LXC) technology on a single platform.
Proxmox features an integrated web-based UI that allows users to manage VMs, containers, and high availability for clusters, with a single tool.
Note: See how Proxmox compares to ESXi, a type-1 hypervisor developed by VMware.
Hyper-V
Hyper-V was developed by Microsoft, and as such, it allows users to create VMs on x86-64 systems running Windows. Each VM runs in its isolated partition, allowing users to simultaneously run multiple VMs on the same hardware.
Hyper-V requires at least one parent partition per hypervisor instance, which creates child partitions with guest operating systems using the hypercall API. The partitions must include a supported Windows Server version (2008 or newer).
The following section includes an overall comparison between Proxmox and Hyper-V.
| Proxmox | Hyper-V | |
|---|---|---|
| Software Type | Open source | Proprietary |
| Basis | Debian Linux KVM | Windows Server |
| Central Management | Yes | Yes |
| Clustering | Yes | Yes |
| High Availability | Yes | Yes |
| Storage and Backup API | Yes | Yes |
| Live Migrations | Yes | Yes |
| VM Load Balancing | Yes | Yes |
| Free Trial | Unlimited | / |
| Pricing | Free with full features | Free with Windows Server. Multiple pricing plans |
Proxmox
Proxmox has many features that continue to expand over time due to its open-source nature. It is a complete solution for enterprise virtualization that integrates a web-based GUI or CLI with Unix shell or Windows PowerShell, facilitating VM management.
Proxmox features include:
KVM Hypervisor and LXC Support. The utility supports the KVM supervisor and Linux Containers (LXC) virtualization technologies.
High-Availability Cluster Manager. HA manager used to manage multiple nodes.
Live/Online Migration. Live migration capabilities ensure low downtime.
Backup. Proxmox Backup Server ensures redundancy and incremental backups for single-file and live restores.
Security. Proxmox features a built-in firewall and storage replication services with separate controls for macros, security groups, aliases, and IP sets.
Third-Party Support. Easy third-party tool integration over a RESTful API.
Multi-Master Policies. Facilitate cluster-wide task deployment and maintenance.
Bridge Networking Model. Supports IPv4 and IPv6 and up to 4094 bridges per host.
Hyper-V
Hyper-V and Proxmox have similar features, with the main difference being the need for multiple management tools in Hyper-V. Windows Server allows users to choose between the GUI-based or Core mode during the installation.
Notable Hyper-V features are:
Nested Virtualization. Allows admins to create VMs with a hypervisor host, facilitating testing and R&D before deploying to a production environment.
Disaster Recovery. Hyper-V Replica is a tool used for creating VM copies and restoring them.
Optimization. Each VM has a set of integration services, facilitating the use of VMs and increasing compatibility.
Portability. Hyper-V supports live migration, storage migration, and VM importing and exporting.
Remote Connection. Hyper-V's Virtual Machine Connection is a tool with console access, providing access to the guest OS.
Security. VM shields and secure boot improve security and protect from malware and unauthorized access.
Checkpoints. Hyper-V allows users to create checkpoints and preserve the state of the VHD, including all the contents, at a point in time. However, there is no data duplication.
Proxmox and Hyper-V provide excellent performance for a wide range of configurations. The following table shows an overview of the key different performance capabilities:
| Proxmox | Hyper-V | |
|---|---|---|
| vCPU Limit | 160 | 64 |
| Logical CPU limit | 768 | 512 |
| Physical Memory Limit | 12TB | 24TB |
| Node Limit | Host-limited | 64 |
As it is open-source, Proxmox offers the same features for free to all users. On the other hand, Hyper-V limits the number of VMs based on the pricing plan.
Note: Read our tutorial and see how to install and configure Proxmox VE.
The latest Windows Server 2019 release offers Hyper-V as a powerful platform for running business-critical workloads. The Persistent Memory feature is the newest addition that boosts Hyper-V's performance and significantly reduces storage latency.
Proxmox offers performance information about clusters, individual nodes, VMs, or containers, all in the web GUI. Seeing all the performance information in a single admin panel allows you to see how resources are distributed across VMs and containers and quickly locate performance bottlenecks.
Proxmox offers the Backup Server tool, allowing users to back up and restore VMs, containers, and hosts at an enterprise level. Hyper-V enables users to back up VMs from the host operating system using the VSS Writer utility or WMI API.
Both hypervisors provide maximum performance if managed by admins who know how to tweak each hypervisor and implement the best performance practices.
Both hypervisors support clustering, which brings numerous advantages. The biggest benefits are migrating VMs between cluster nodes and managing multiple servers from one interface.
Note: Learn the difference between a container and a VM.
Proxmox
Proxmox allows users to manage multiple servers using its web-based management GUI. The GUI is beneficial when managing server farms. The Proxmox Cluster Manager utility provides additional security using various authentication methods and enables users to migrate VMs and containers in the cluster.
There is no limit to the number of nodes in a cluster, except for the host configuration and network performance. Increase availability by setting up multiple Proxmox servers.
Note: Deploy multiple virtualization servers in under 10 minutes using Proxmox on a pre-configured Arosscloud Bare Metal Cloud instance.
Windows Server 2019 is available too, and typically deploys in 15 minutes.
Hyper-V
Hyper-V supports clustering through its Failover Cluster Manager utility, which comes free with Windows Server, and allows users to build and manage failover clusters. Failover clustering maintains high availability of business-critical applications.
Another tool facilitating Hyper-V clustering is the System Center Virtual Machine Manager (SCVMM) utility. However, SCVMM isn't included with Windows Server, and it must be purchased separately.
SCVMM enables users to manage Hyper-V hosts and failover clusters at a scale too large for Hyper-V manager. It combines multiple management tasks in a single tool with a user-friendly interface and an analytics dashboard.
Note: Check out our tutorial on how to install Ubuntu on Windows with Hyper-V, or install Windows 11 on a Hyper-V VM.
Proxmox
Proxmox is based on Linux (Debian), making it easy to use if you have previous experience working with Linux. Additionally, its integrated web-based GUI facilitates the management of all tasks in a single place. The web interface is based on ExtJS and supports all modern browsers.
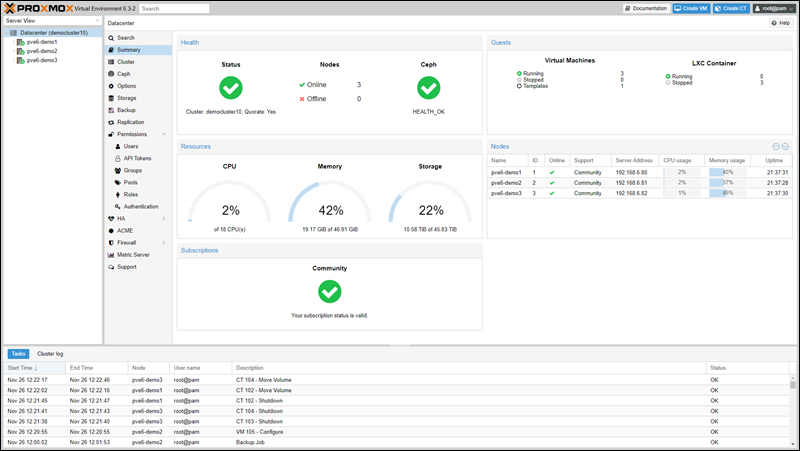
However, the Proxmox Admin is still under development, and some advanced options require command-line use.
Hyper-V
Being a Microsoft product, Hyper-V is intuitive and easy to use. However, task management is distributed across five management tools.
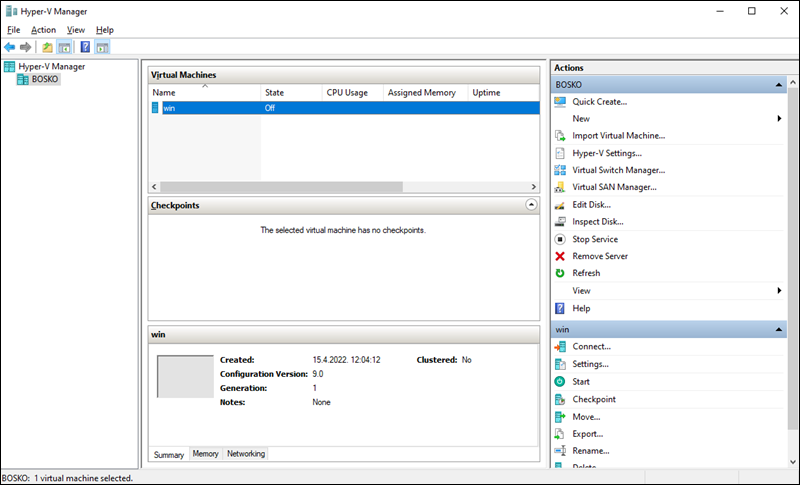
For example, it is very easy to create a VM, but managing it and performing various maintenance tasks requires different interfaces. This applies particularly to clustering, as it requires several different tools to perform all the necessary tasks - including Hyper-V Manager and Failover-Cluster Manager.
The Hyper-V Manager utility provides the basic VM functions - creation, retrieval, updating, or deletion. However, it is limited in terms of moving VMs between hosts and having few performance metrics available. Advanced functionality requires installing additional tools.
Proxmox
Proxmox supports many image formats, including HDD, QCOW, QCOW2, QED, VDI, etc. The support for a wide range of images facilitates VM portability and OS support in the guest VM.
However, importing and exporting an image requires advanced command-line usage as well as the Proxmox Backup Server utility. The easiest way to move an image is to back up a configuration on the current VM and restore it on another one.
Hyper-V
Hyper-V provides a Live Migration feature that allows users to move running VMs from one host to another without downtime. Use the Live Migration feature when applying patches or when you want to move a VM to a host with more available resources due to increased demand.
Hyper-V saves the guest OS to a single virtual hard disk file, supporting the VHD and VHDX formats. After migrating the guest OS, it detects any hardware changes via the integration services and installs the necessary drivers to improve performance.
Hyper-V also allows users to create and use VM templates. The templates are generic VM copies that can be used to create a new VM with the same characteristics.
Proxmox
Proxmox is Linux-based, which means it comes with built-in enterprise-level security features. It provides automated backups for user-specified nodes while isolating VMs within containers, thus protecting other VMs from potential issues or malicious code in one VM.
The Proxmox Backup Server utility encrypts data and all client-server traffic, thus protecting data integrity. By limiting user access based on their role, Proxmox prevents unauthorized access and reduces the chance of human error.
The open-source community continuously singles out priority issues, bugs, or security gaps, helping Proxmox developers address them quickly.
Hyper-V
Hyper-V offers the virtual switch application for free. The virtual switch is an integral part of virtual networking, which enables VMs to communicate with each other. The virtual switch inspects each data packet sent between VMs before routing it, thus improving security in the virtual environment.
In addition, from Windows Server 2019, all traffic on the entire subnet is encrypted without requiring any modifications to VMs or network equipment.
Hyper-V improves data security with shielded VMs, encrypted with BitLocker, which helps secure the virtual disks. The encryption prevents booting the disk on another VM or reading the data contained in the virtual drive.
Proxmox
While Proxmox offers all its features for free, professional support from the Proxmox technical team requires a paid Proxmox VE subscription. The subscription also provides access to the Proxmox Enterprise Repository and regular software updates and security improvements.
For users who purchase a paid subscription, Proxmox also offers the option to book training for system administrators or submit tickets when they encounter issues.
However, if the paid subscription is not within your budget, you can likely resolve your issue by searching the Proxmox Wiki or looking for answers in the developed Proxmox community.
Hyper-V
Hyper-V has excellent support on the internet as developers worldwide use it. Many forums, help websites, blogs, community sites, and knowledge bases contain answers to various issues users may encounter using Hyper-V.
Alternatively, get help directly from Microsoft with timely responses and support techs if you have an active support agreement with Microsoft.
Proxmox
Proxmox is free with an optional paid subscription that provides users access to the enterprise repository and professional support from Proxmox developers.
At the time of writing this article, the available subscription plans are as follows:
| License Level | Cost and Support Options |
|---|---|
| Community | €95 per year and CPU socket |
| Basic | €295 per year and CPU socket Three support tickets per year. |
| Standard | €445 per year and CPU socket Ten support tickets per year. |
| Premium | €890 per year and CPU socket Unlimited support tickets. |
Hyper-V
While Hyper-V is free to download as a standalone virtualization platform, any management features require an upgrade to one of the full Windows Server editions and a System Center purchase.
Licensing Windows Server Datacenter on the Hyper-V host lets you deploy as many virtualization servers as your bare metal server configuration allows.
While basic features like creating a VM, creating snapshots, and allocating resources are free, Microsoft recommends an upgrade to Windows Server and a Windows System Center purchase to manage the server.
The costs are:
Windows System Center license - starting from $1,323 per year.
Windows Server 2019 license - $501 per year for the Essentials edition, $972 for the Standard edition, and $6,155 for the Datacenter edition with full virtualization features.
While both hypervisors are the same type and run on bare metal servers, they usually cater to different audiences. There are several key factors to consider when choosing a hypervisor for your organization:
The organization's size.
Scalability options.
Budget impact.
Performance (includes clustering, backups, and portability).
Ease of use.
Server management.
Proxmox is a good choice for organizations requiring more in-house control with a tight budget. The only expense is the optional subscription for official support and enterprise repository access. It is based on Linux, making it intuitive and easy to use if you are accustomed to a Linux OS.
On the other hand, Hyper-V is a good choice for organizations with admins well-versed with the Microsoft product stack, as there will be no need for additional training.
If you have already purchased a Windows Server edition, the Hyper-V license is already included for free. However, the platform comes with additional costs for VM management tools, so consider the budget impact.